LCI Monthly – What Shaped October 2025
Economy & Politics
Global Business Activity Strengthens as Germany and U.S. Lead October Growth Momentum
In October, the German economy grew at its fastest pace in nearly two and a half years, driven mainly by strong momentum in the services sector. The composite PMI rose to 53.8, well above the 50 growth threshold, while the services PMI climbed to 54.5. Manufacturing remains slightly below expansion at 49.6, with weak exports and modest job cuts. Across the Eurozone, growth accelerated, with the composite PMI reaching a 17-month high of 52.2, supported by the strongest rise in new orders since 2022. France’s industry stabilized, though services weakened amid political gridlock. In the UK, manufacturing rebounded to 49.6 ahead of the government’s November budget. Japan’s private sector lost momentum (PMI 48.3), while India’s industry remained strong (58.4). The U.S. economy continued expanding, with its composite PMI rising to 54.8 and services surging to 55.2, implying an annualized GDP growth rate of around 2.5%.
U.S. Inflation Rises to 3%
Consumer prices rose by 3% in September compared to the same month last year. Economists surveyed by Reuters had expected an even higher increase of 3.1%, following a 2.9% rise in August. On a monthly basis, prices climbed by 0.3% from August to September. Core inflation — which excludes the volatile prices of energy and food — stood at 3% in September.
U.S. Regional Bank Troubles Spark Market Concerns Again
A new wave of bankruptcies and loan losses is unsettling U.S. markets, raising fresh concerns over the financial stability of regional banks. Western Alliance and Zions Bancorp both reported major credit losses this week, with Zions writing off $50 million in bad loans at its California Bank & Trust subsidiary. The news came just as large U.S. banks reported solid profits, but JPMorgan CEO Jamie Dimon warned that “if one cockroach appears, there are likely more,” referring to hidden risks in private credit and leveraged loans. Recent bankruptcies, such as auto suppliers Tricolor and First Brands, revive memories of the 2023 regional banking crisis following the Silicon Valley Bank collapse. While today’s environment differs—interest rates are falling rather than rising—credit spreads remain narrow, suggesting investors underestimate risk. Analysts caution that these isolated failures may signal a late-cycle market vulnerable to correction.
China Tightens Control Over Rare Earth Exports, Raising Global Supply Concerns
China is tightening its grip on the global supply of rare earth elements (REEs), expanding export restrictions from seven to twelve of the seventeen key elements as of December 1. From then on, any product containing more than 0.1% Chinese rare earths will require government approval to export. This affects industries ranging from magnets, catalysts, and solar panels to semiconductors and military technology. China dominates global refining capacity—processing 85% of light and virtually 100% of heavy rare earths—even though only about 70% of the metals are mined domestically. The country’s dominance stems from massive state investment, economies of scale, and tolerance for the environmental costs of extraction. The green energy transition is driving demand for REEs used in electric vehicles and wind turbines. Meanwhile, the government is consolidating the industry under major state-controlled groups to tighten oversight. Although new mining projects are emerging in the U.S., Australia, and Europe, production remains limited. Developing new mines can take a decade, and despite growing recycling efforts, China’s export restrictions continue to give it strategic leverage—allowing it to exert pressure not only on the U.S. but also on the global economy.
U.S. Sanctions on Russian Oil Giants Reshape Global Energy Trade
The U.S. government has imposed sweeping sanctions on Russia’s energy sector, targeting major oil producers Lukoil and Rosneft along with their subsidiaries. Companies worldwide continuing to trade with them risk U.S. secondary sanctions, including exclusion from American financial markets. Business partners have until November 21 to cut ties, causing oil prices to surge 5% as markets anticipate tighter global supply. The move aims to weaken the Kremlin’s key revenue source and pressure President Vladimir Putin to change course in the war against Ukraine. The sanctions significantly affect China and India, Russia’s largest oil buyers. China imports 2.3 million barrels daily, while India now sources over 30% of its oil from Russia. Major firms such as Reliance and Nayara—the latter part-owned by Rosneft—face the dilemma of complying with U.S. restrictions or losing access to Western markets. Analysts expect both countries to increasingly turn to suppliers in the Middle East, Africa, and South America, likely pushing prices higher. While India’s refiners may see lower profits, the broader economy should remain stable. The sanctions mark a major shift in global oil flows, highlighting Washington’s growing leverage over Moscow’s remaining energy trade partners.
Sanae Takaichi Becomes Japan’s First Female Prime Minister Amid Political Upheaval
Japan has elected Sanae Takaichi, 64, as its first female prime minister, ending months of political uncertainty following former leader Shigeru Ishiba’s resignation. Takaichi, representing the conservative Liberal Democratic Party (LDP), won 237 of 465 parliamentary votes—more than her coalition’s total—thanks to a new alliance with the Japan Innovation Party (Ishin). Domestically, Takaichi faces a fragmented political landscape after the Buddhist-backed Komeito party quit its decades-long coalition with the LDP. Her partnership with Ishin provides only conditional support, leaving her mandate fragile. Economically, she favors expansionary fiscal and monetary policies similar to her mentor Shinzo Abe, but rising debt, inflation, and a weak yen limit her room to maneuver. Takaichi’s victory signals a conservative resurgence. Her agenda includes constitutional reform, a tougher stance on China, and strengthening Japan’s defense. However, internal divisions—especially with fiscal hawk Taro Aso, now her deputy—and uncertain public support could hinder her ability to deliver. Japan enters a new era led by its first female premier, but stability remains far from assured.
Government Crisis in France: Lecornu Survives No-Confidence Vote and Can Continue Governing
In France, Prime Minister Sébastien Lecornu survived a no-confidence vote and will remain in office. He secured the Socialists’ support by announcing the suspension of President Emmanuel Macron’s controversial pension reform. The gradual increase of the retirement age from 62 to 64 will be frozen at the current 62 years and 9 months, a move hailed as a triumph by the Socialist Party.
Credit Suisse Creditors Win Court Battle: AT1 Bond Write-Off Ruled Illegal — But Who Will Pay Them Back?
Creditors of Credit Suisse have won a major victory: the Federal Administrative Court has ruled that the CHF 16 billion write-off of AT1 bonds during the bank’s takeover was unlawful. However, it remains uncertain whether — or when — investors will receive any compensation.
Gold Price Hits New Record, Surpasses $4,000 per Ounce
The price of gold continues to reach new record highs, having now surpassed the $4,000 per ounce mark. The main drivers are the tense geopolitical situation, a weak U.S. dollar, central bank purchases, high government debt, and fears of inflation. Gold has a millennia-old tradition as a store of value and a classic “crisis currency.”
U.S. Shutdown Could Become the Longest in History
Hundreds of thousands of federal employees have been on leave or working without pay since October 1, as Republicans and Democrats failed to agree on a new budget. The U.S. government has effectively come to a standstill, resulting in airport delays, closed museums, and a halt to farm loans. The standoff threatens to turn into the longest government shutdown in U.S. history.
Milei Strengthens His Mandate but Faces Political Challenges Ahead
Argentine President Javier Milei achieved a surprisingly strong election victory, securing a solid mandate to continue his economic reforms. His libertarian coalition now controls about one-third of Congress, allowing him to govern by decree on economic matters and prevent opposition overrides. Voters signaled they reject a return to Peronist policies despite recent economic hardships. Milei’s early reforms produced impressive results: inflation dropped from 200% to around 30%, the fiscal deficit turned into a surplus, and growth briefly returned, enabling partial easing of currency controls. However, since May, the economy has contracted again, the peso required U.S. loans for stabilization, and corruption scandals have hurt his approval, now around 40%. Although Milei’s win restores confidence, he still lacks a majority in Congress. To sustain reforms, he must build broader alliances and show more political tact—something his confrontational style has often undermined.
U.S. Escalates Conflict with Venezuela: Pentagon Deploys Its Most Powerful Aircraft Carrier to the Caribbean
The Trump administration is intensifying its confrontation with Venezuela, ordering the aircraft carrier USS Gerald R. Ford—the most powerful in the U.S. Navy—to the Caribbean. The Pentagon is also reportedly considering strikes on targets inside Venezuela, marking a sharp escalation in tensions. The move underscores Washington’s growing willingness to use military pressure against the government in Caracas, following years of diplomatic and economic sanctions.
“Perfect Match” but “Significant Risk”: Novartis Announces Its Largest Acquisition in a Decade
Swiss pharmaceutical giant Novartis has unveiled its biggest takeover in ten years, announcing plans to acquire U.S.-based Avidity Biosciences for $12 billion. The Basel-based company describes the deal as a “perfect match,” expecting it to fuel future growth and strengthen its position in cutting-edge therapies. Avidity specializes in RNA-targeted medicines, a promising but still experimental field aimed at treating rare muscular and genetic diseases. However, none of Avidity’s drugs have yet reached the market, making the acquisition a high-stakes bet on future innovation rather than immediate profit.
Fed Cuts Rates but Signals Pause Ahead Amid Strong U.S. Growth and Labor Market Uncertainty
The Fed cut interest rates by 0.25% to a range of 3.75–4% to cushion the U.S. economy amid a government shutdown and limited economic data. While inflation remains elevated, it is not spreading broadly, and the main weakness lies in the labor market, partly due to reduced immigration and retirements. The decision was divided, with some favoring a larger cut and others none at all, signaling uncertainty about further easing. Fed Chair Jerome Powell emphasized that another cut in December is “far from certain,” especially as GDP and consumer spending have been stronger than expected, growing 3.8% and 2.5%, respectively. The Fed also ended its balance sheet reduction program due to tight liquidity. Markets now expect fewer rate cuts in 2025, and the Fed is likely to pause if growth and consumption remain robust.
Daring Heist at the Louvre: Thieves Steal France’s Crown Jewels in Just Seven Minutes
Burglary at the Paris Louvre: In only seven minutes, thieves made off with eight of France’s crown jewels. The perpetrators entered through a window using a freight elevator and stole, among other items, jewelry that once belonged to Empress Eugénie.
the German economy grew at its fastest pace in nearly two and a half years
Markets
Fixed Income
Eurozone
Eurozone government bond yields eased slightly in October as softer inflation data and weak business sentiment strengthened expectations that the ECB will begin cutting rates in early 2026. The German 10-year Bund yield retreated to around 2.65 %, while aggregate euro area yields edged lower to 3.1 %. In France, political tensions persisted following the earlier government crisis, but market reactions remained contained. OAT yields hovered near 3.5 %, with spreads versus Bunds broadly stable. Peripheral bonds outperformed modestly, supported by improving risk sentiment and continued ECB reinvestments under the PEPP program.
USA
U.S. Treasury yields declined further in October after the Fed cut rates by 25 bps to a range of 3.75–4.0 %, while signaling that additional easing was “far from certain.” Softer inflation readings and signs of labor-market weakness supported the move, though resilient GDP and consumer spending kept longer yields from falling sharply. Credit spreads remained tight, supported by strong risk appetite and steady demand for investment-grade issuance. High-yield bonds also outperformed, reflecting investors’ confidence that the economy is slowing, but not sliding into recession.
Equity
Global Overview
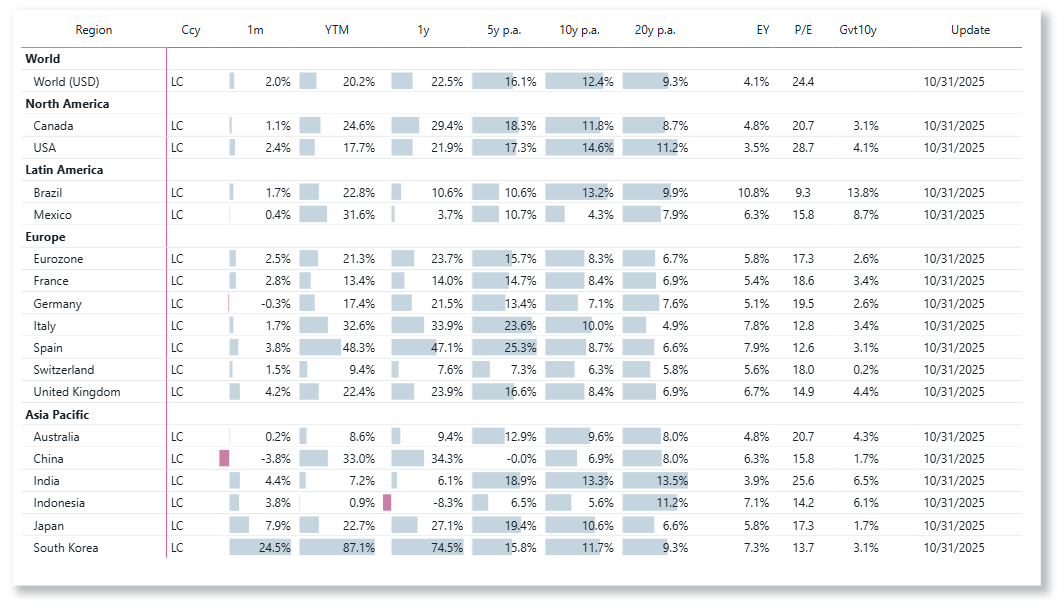
Global equities advanced further in October, with the MSCI World Index up about 2.0 %. Markets reacted positively to the Fed’s rate cut and continued disinflation across major economies. Robust U.S. growth and resilient corporate earnings supported sentiment, while European and Japanese equities benefited from improved confidence and currency stability. Emerging markets were mixed, weighed down by a stronger U.S. dollar and uneven growth momentum in China.
Europe
European equities advanced overall in October, with the Eurozone up 2.5 %. France gained 2.8 %, supported by strength in luxury, health care, and consumer sectors, while Germany slipped 0.3 % as industrials and exporters remained under pressure from weak global demand. Italy (+1.7 %) and Spain (+3.8 %) outperformed, driven by resilient domestic activity and solid bank results. Switzerland (+1.5 %) recovered modestly, helped by defensive sectors and renewed investor demand for quality growth stocks. The UK (+4.2 %) led regional gains, benefiting from broad-based advances in financials, consumer discretionary, and energy. Overall, European markets rose on easing inflation expectations and renewed confidence in the region’s near-term outlook.
North America
North American equities advanced in October, with the U.S. up 2.4 % and Canada 1.1 %. In the U.S., the Fed’s rate cut and easing inflation supported sentiment, while information technology and health care delivered strong gains. Financials underperformed amid renewed stress in some regional banks and narrowing net interest margins, while energy and materials weakened on softer commodity prices. In Canada, modest gains in industrials were offset by weakness in financials and resources. Overall, the region continued to benefit from resilient growth expectations and improving monetary conditions.
Asia-Pacific
Asian equities advanced strongly in October, though performance remained highly uneven across markets. South Korea (+24.5 %) surged on a powerful rebound in semiconductor and technology stocks, supported by improving export data and strong foreign inflows. Japan (+7.9 %) also outperformed, driven by a weaker yen, robust corporate earnings, and expectations of continued monetary accommodation. India (+4.4 %) maintained solid momentum on resilient domestic growth, while Indonesia (+3.8 %) recovered with help from energy and materials. In contrast, China (-3.8 %) declined as property-sector stress and subdued consumer sentiment overshadowed policy support measures. Australia (+0.2 %) was little changed, with mining and financials offsetting weakness in defensive sectors.
Latin America
Latin American equities edged higher in October, with Brazil up 1.7 % and Mexico gaining 0.4 %. In Brazil, moderate gains reflected steady domestic sentiment and expectations of continued policy continuity following recent fiscal adjustments. A stable real and easing inflation supported selective buying in financials and consumer sectors, though energy and materials lagged amid softer commodity prices. In Mexico, markets consolidated after strong prior-month gains, as investors assessed the impact of a firm peso and cautious guidance from Banxico. Broader regional sentiment remained underpinned by contained inflation and resilient domestic demand, even as the stronger U.S. dollar limited upside momentum.
Equity Performance of selected Countries
Learn more on LCI Research
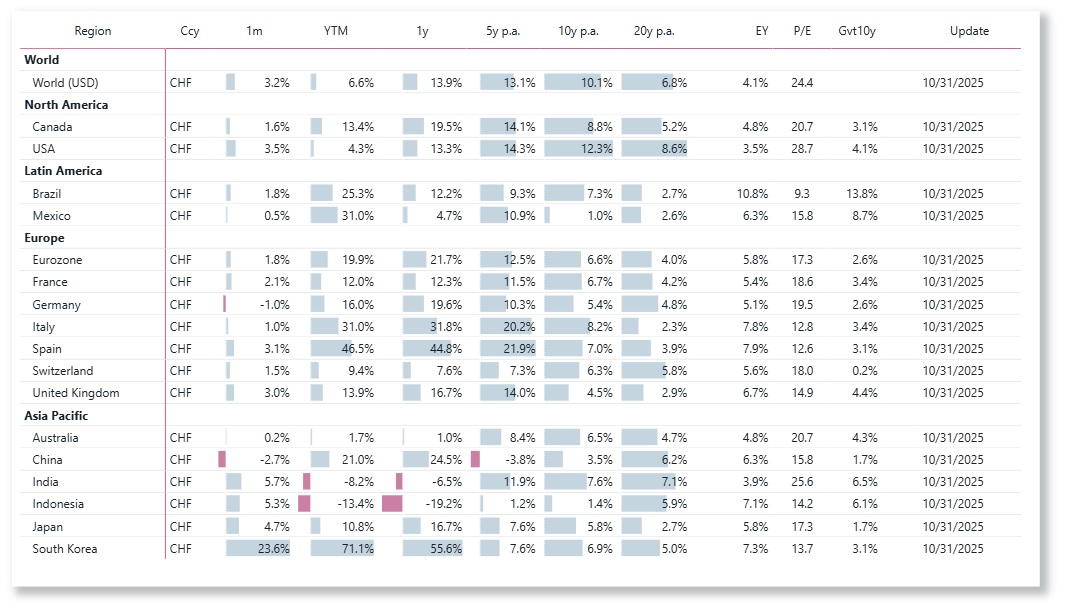
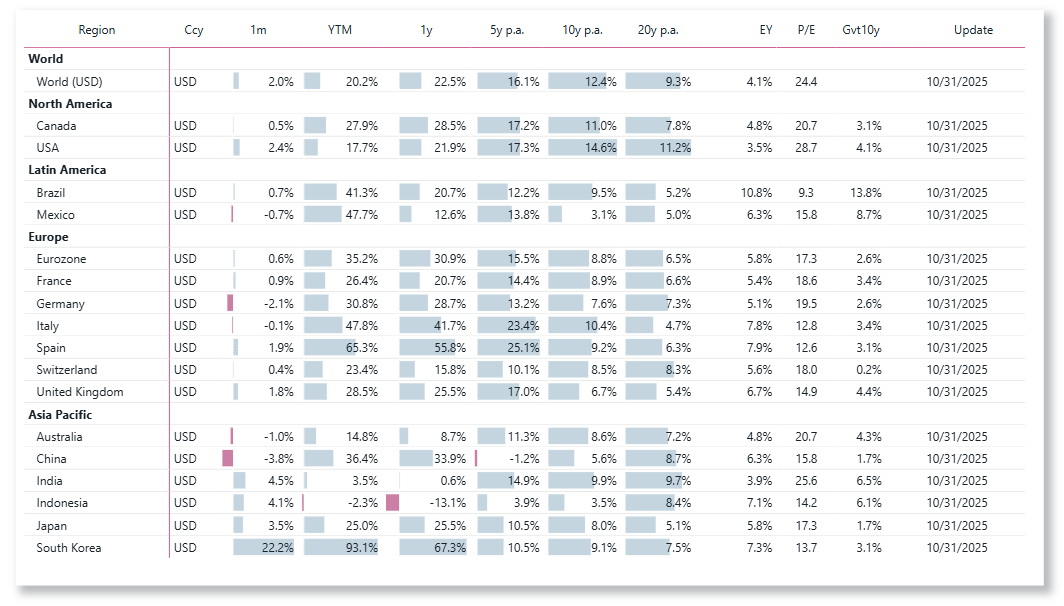
Choose the performance be computed in local currency, CHF, EUR or USD
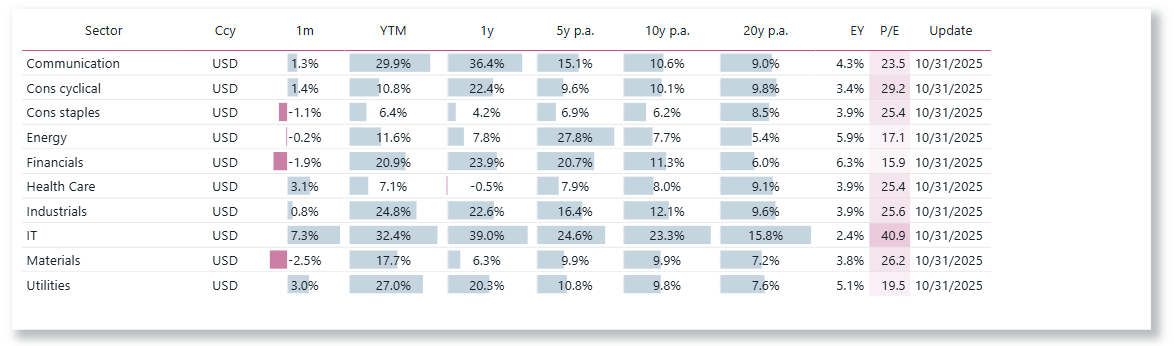
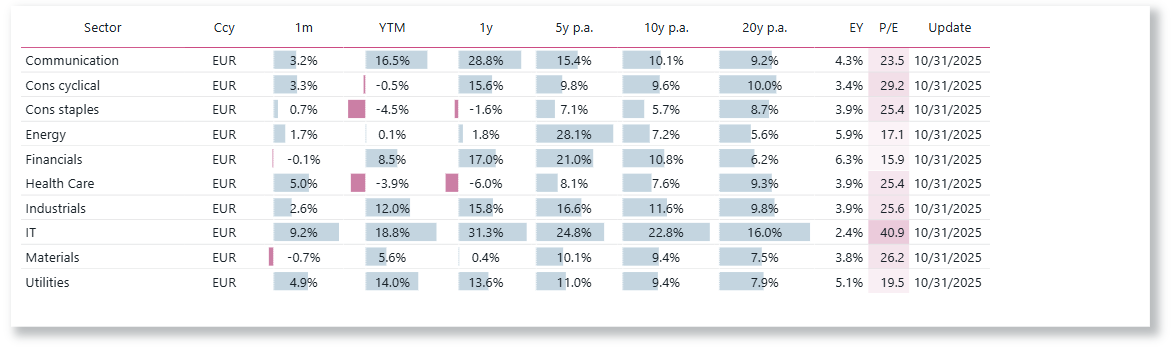
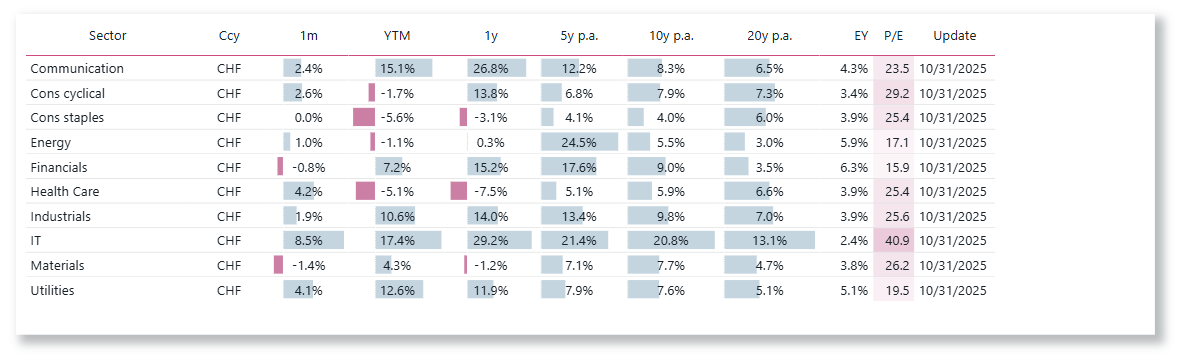
Equity Performance of Global Sectors
Choose the performance be computed in USD, EUR or CHF
Learn more about LCI Strategies
LCI Strategies Performance update
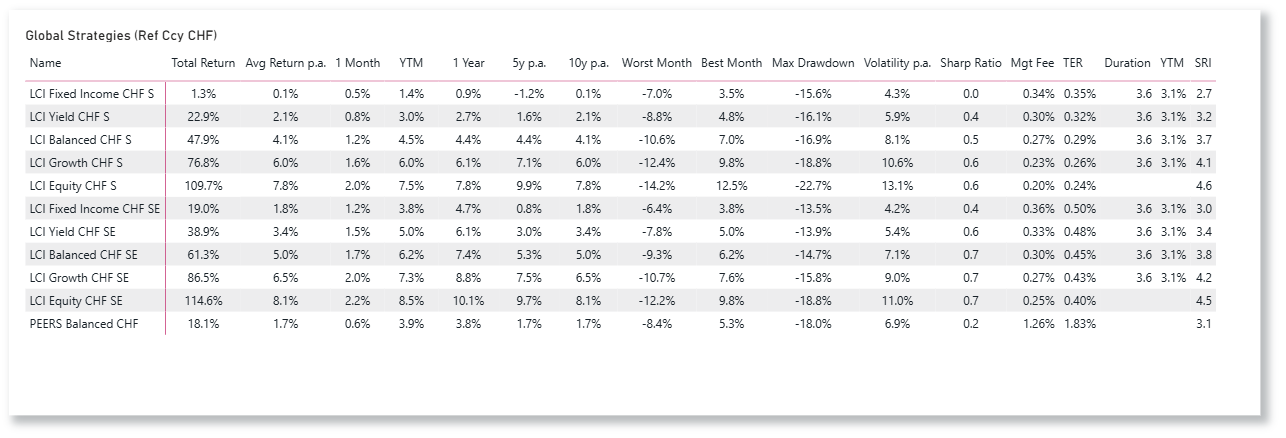
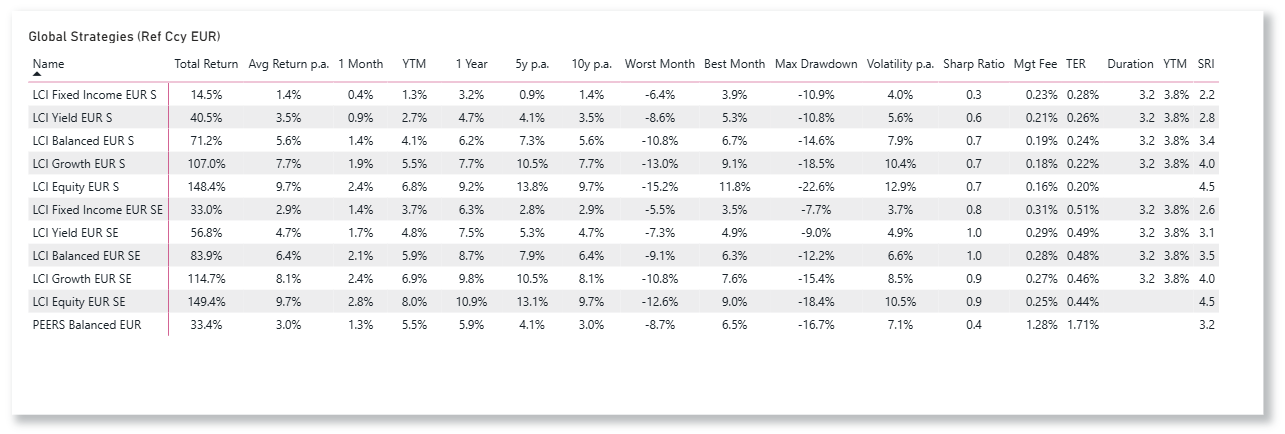
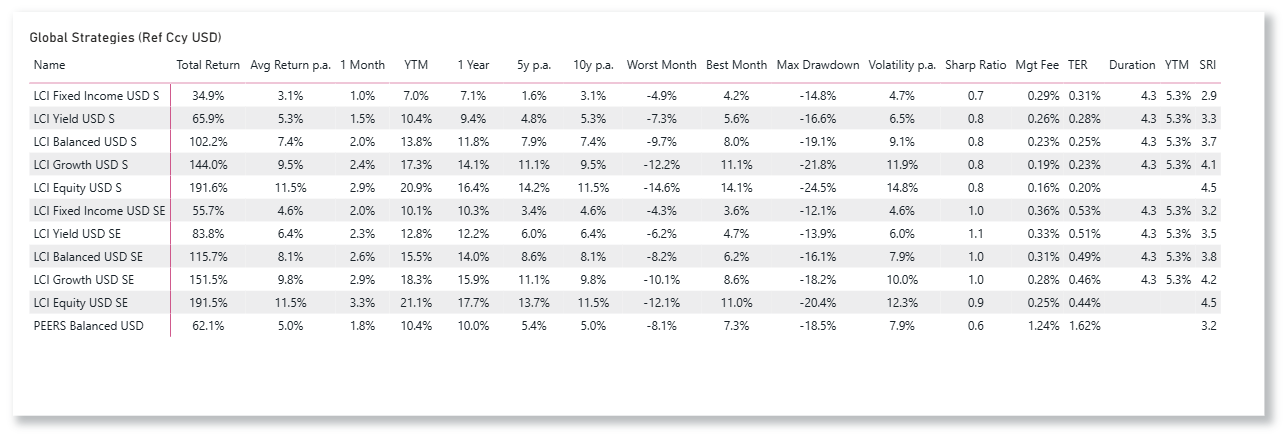
LCI Strategies in CHF, EUR and USD